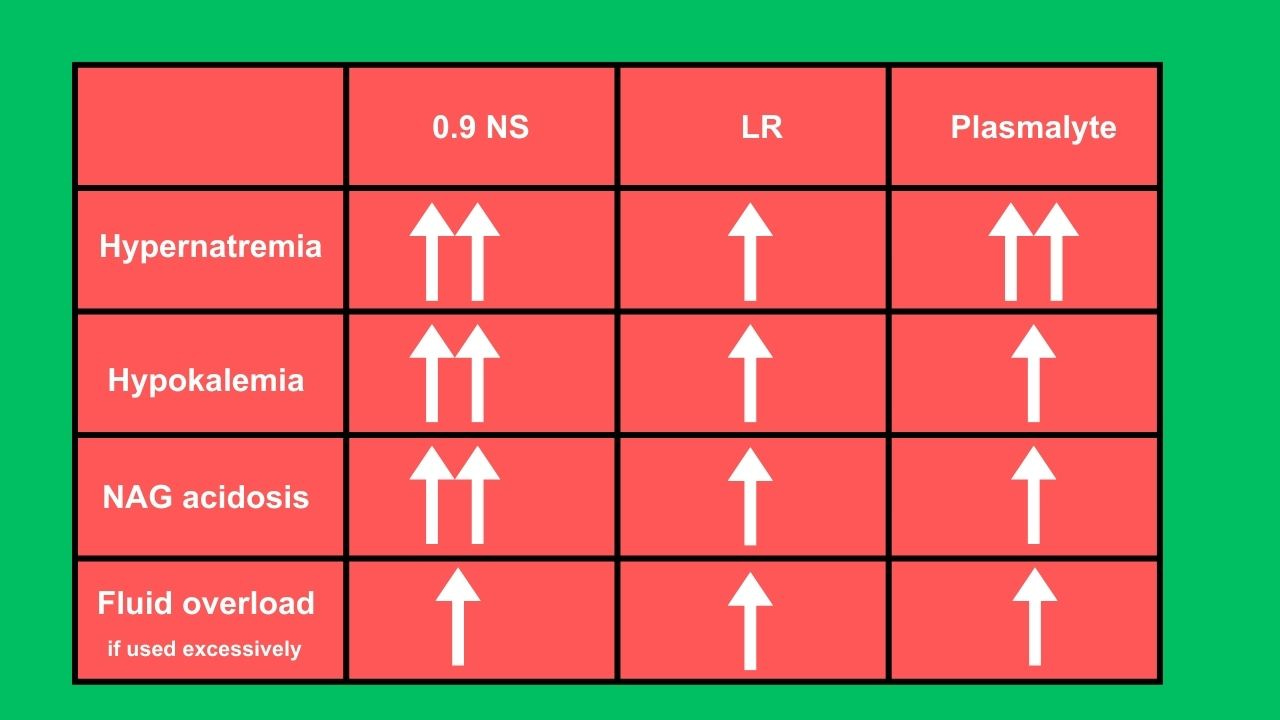
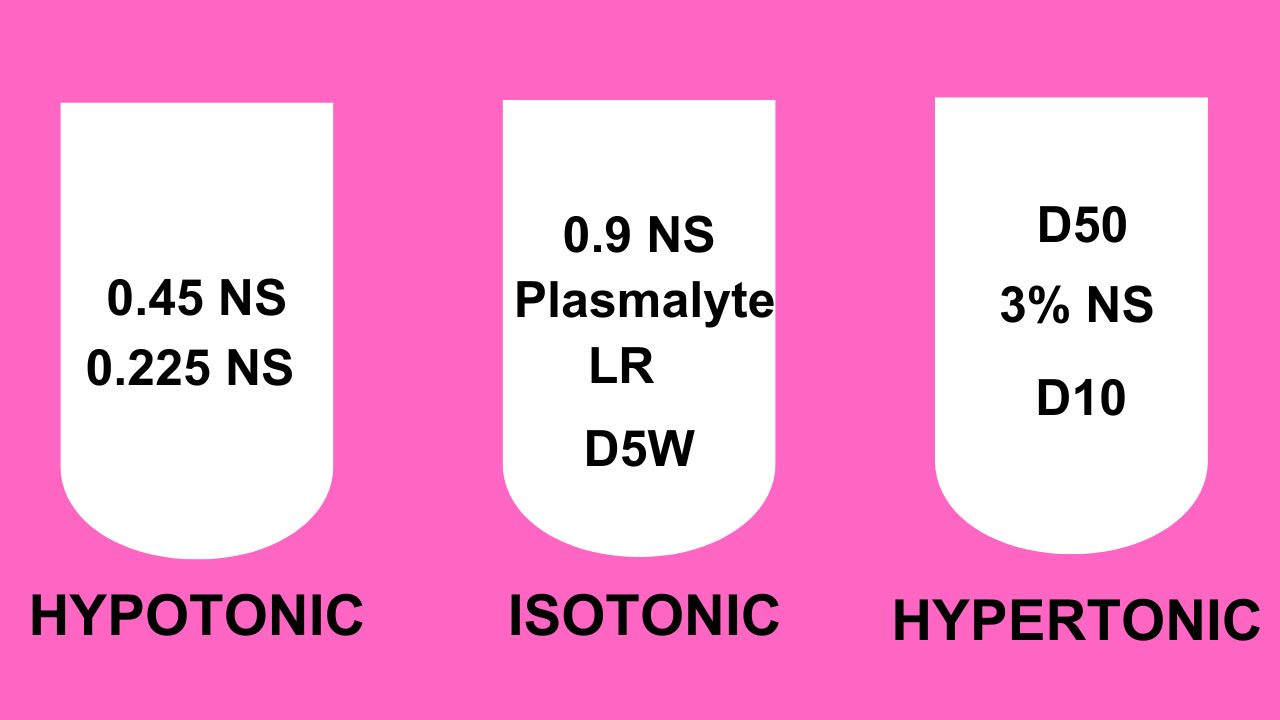
Saline solutions
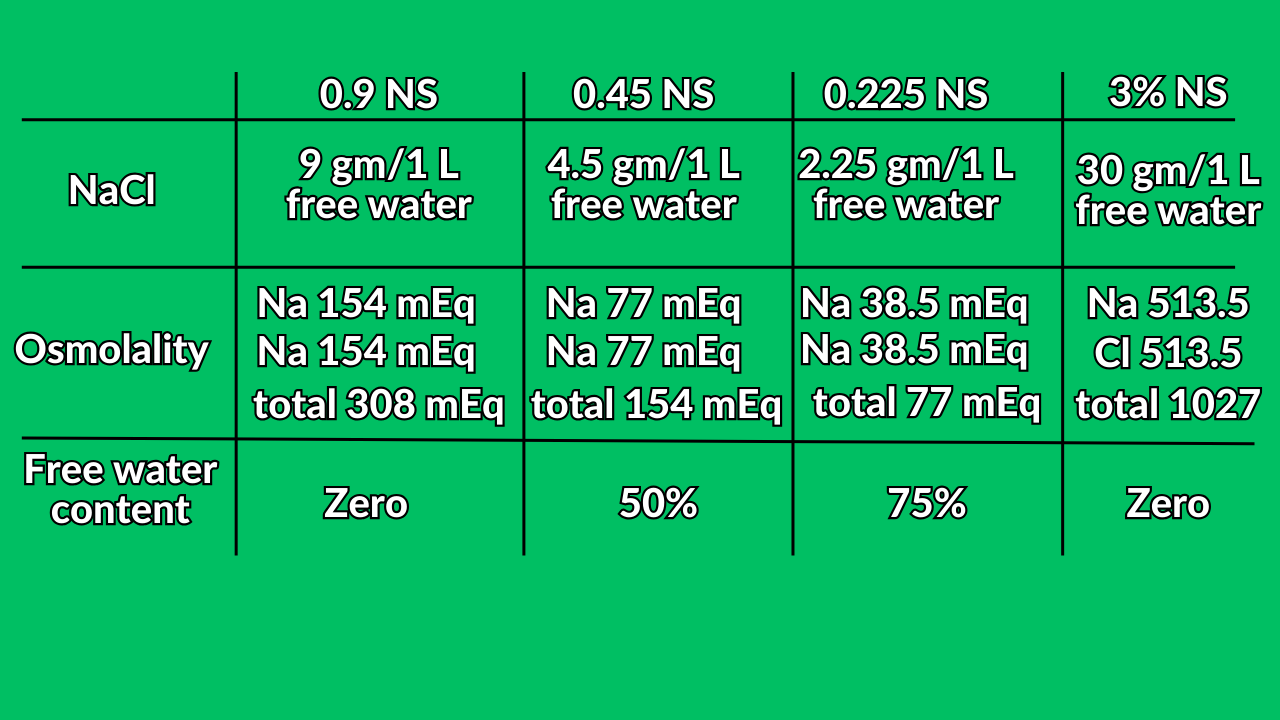

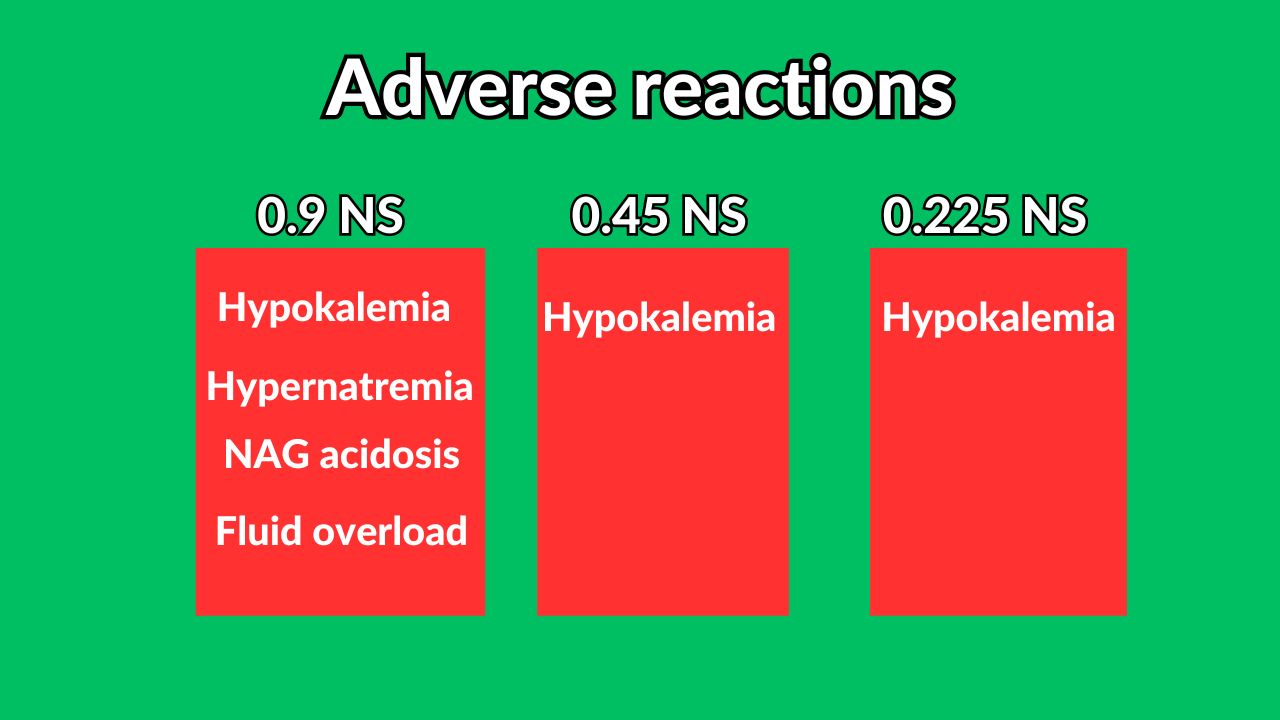
- 500 ml of 0.9 NS + 500 free water = 1000 ml of 0.45 NS.
- 500 ml of 0.45 NS + 500 free water = 1000 ml of 0.225 NS.
- 250 ml of 0.9 NS + 750 free water = 1000 ml of 0.225 NS.
Balanced solutions:
These are solutions that mimic the human’s serum plasma.
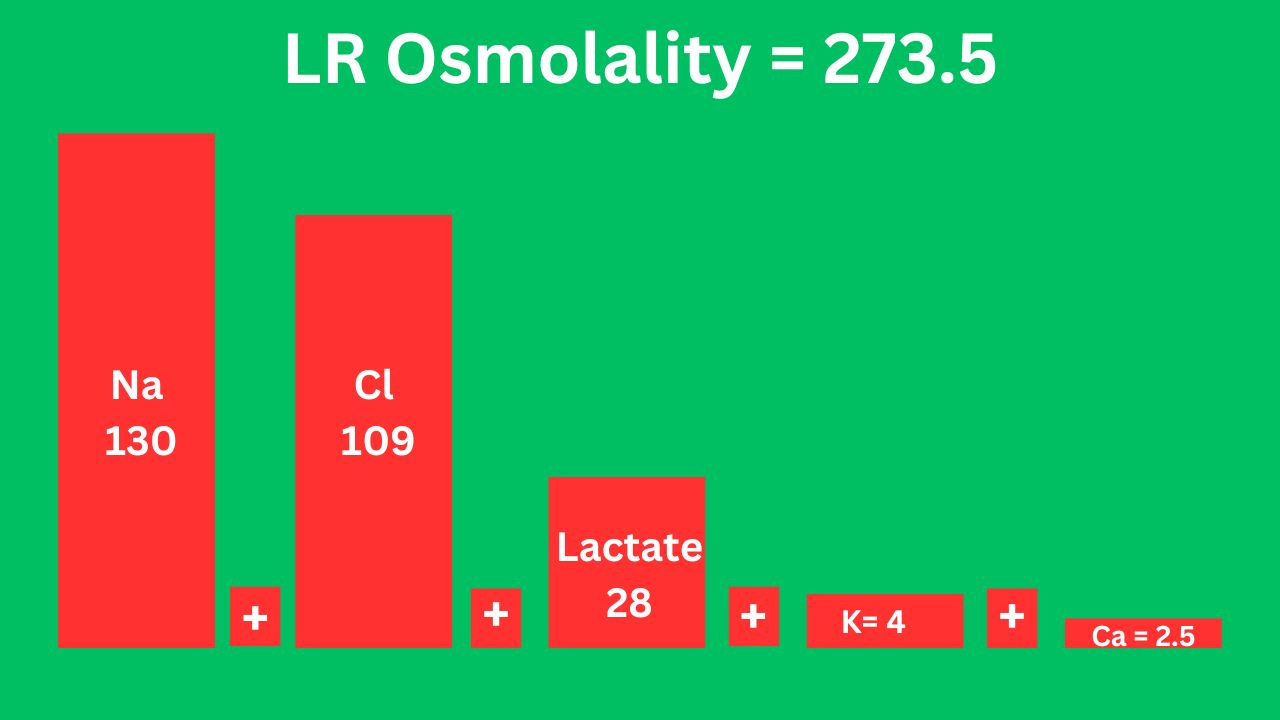
Lactated ringer (LR)
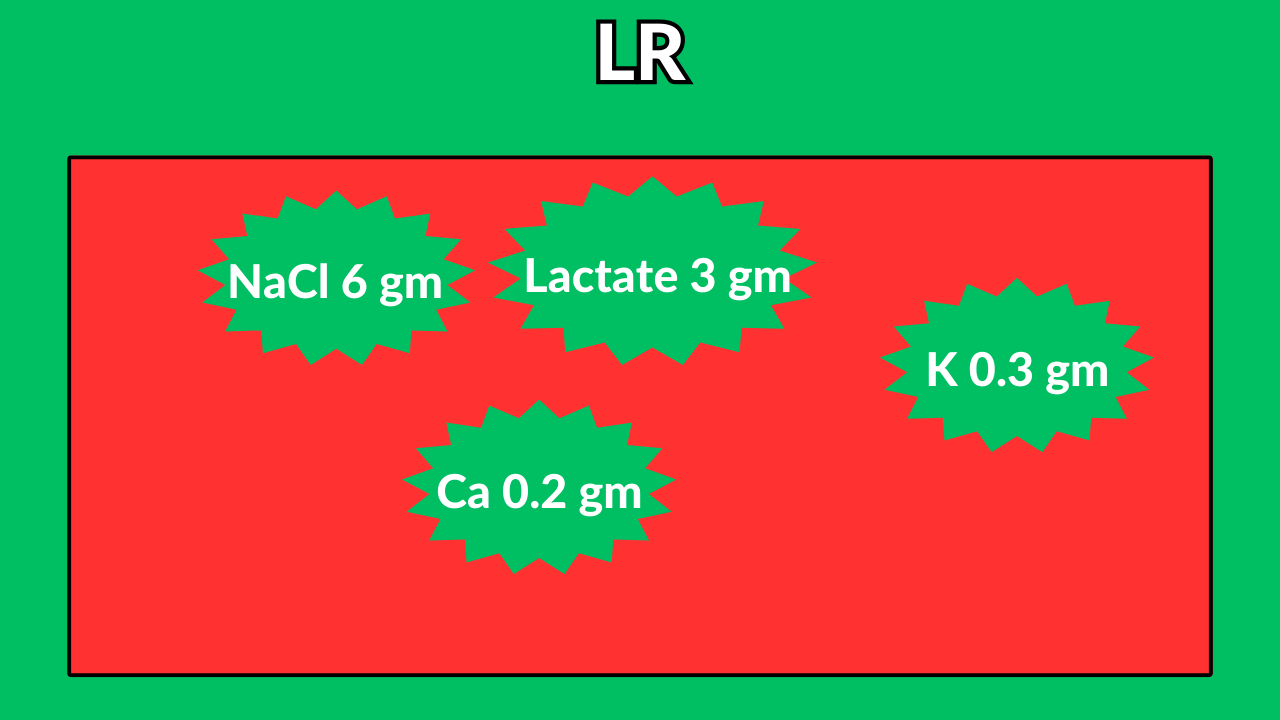
Lactate is a precursor of bicarb.
Plasmalyte
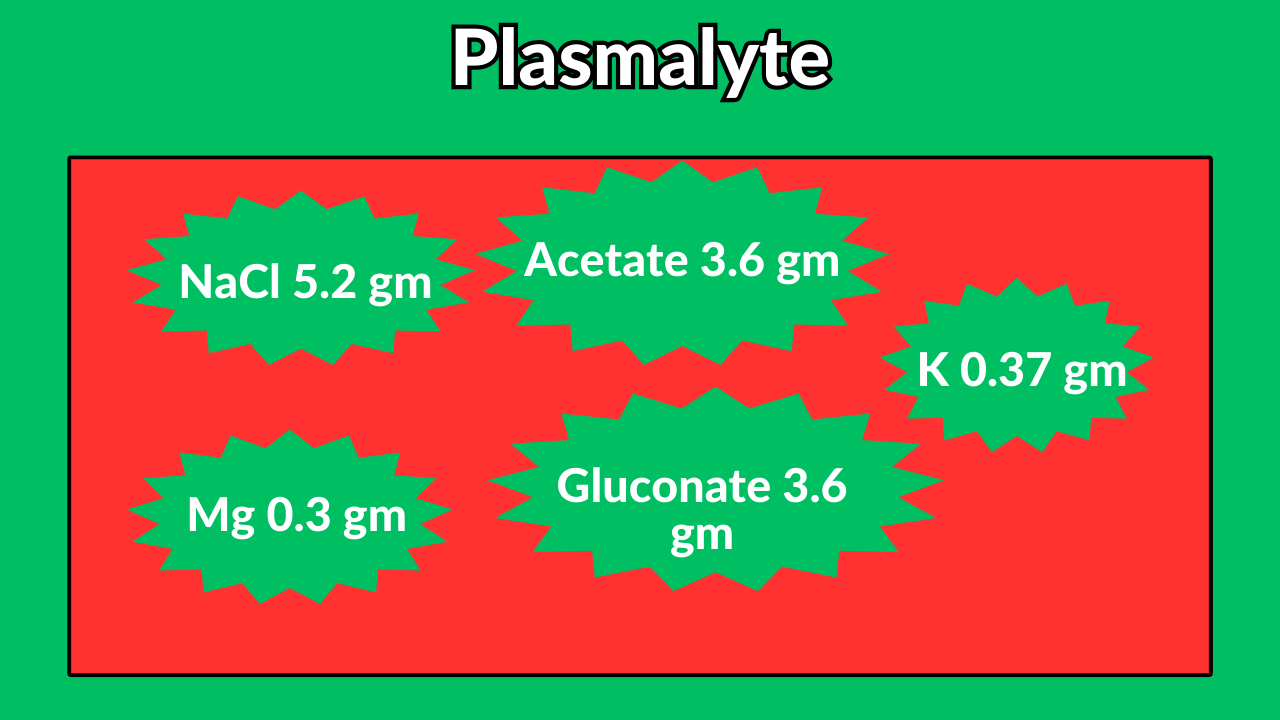
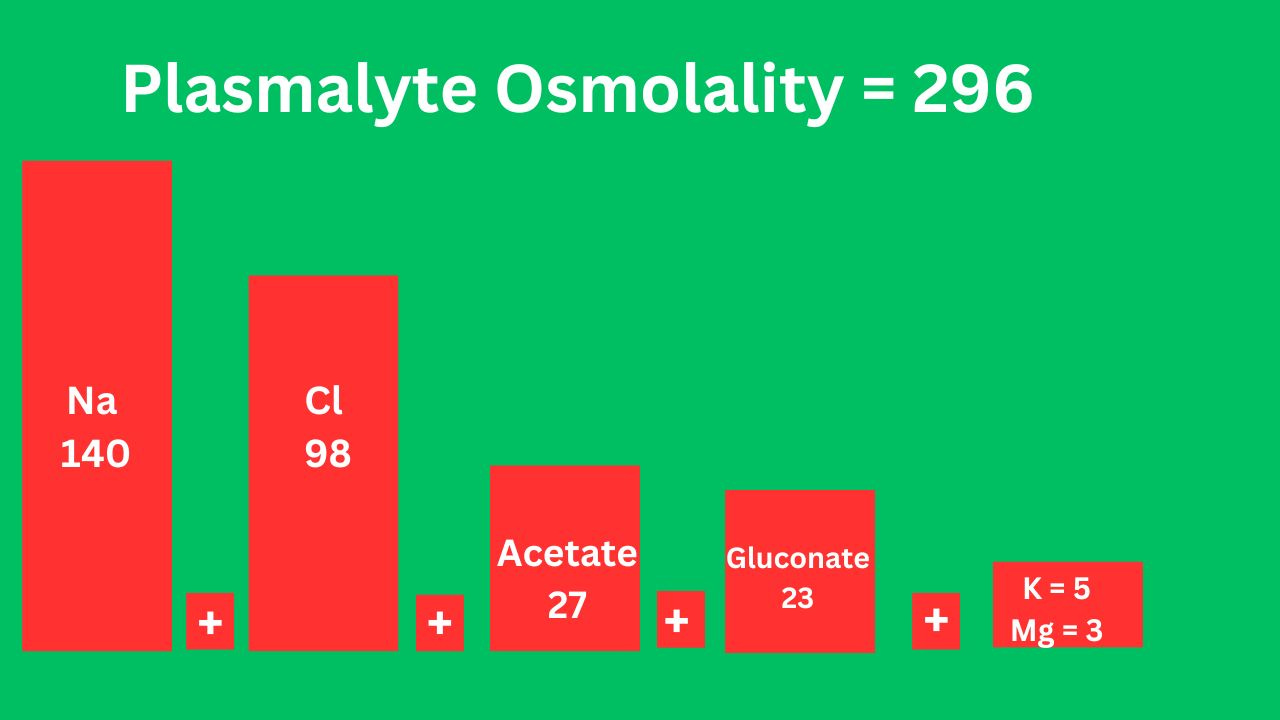
Acetate is a precursor of bicarb.
Dextrose solutions
Ingredients:
- 5% dextrose = 50 gm glucose/1000 ml free water.
- 10% dextrose = 10 gm glucose/1000 ml free water.
- 50% dextrose = 500 gm glucose/1000 ml free water.
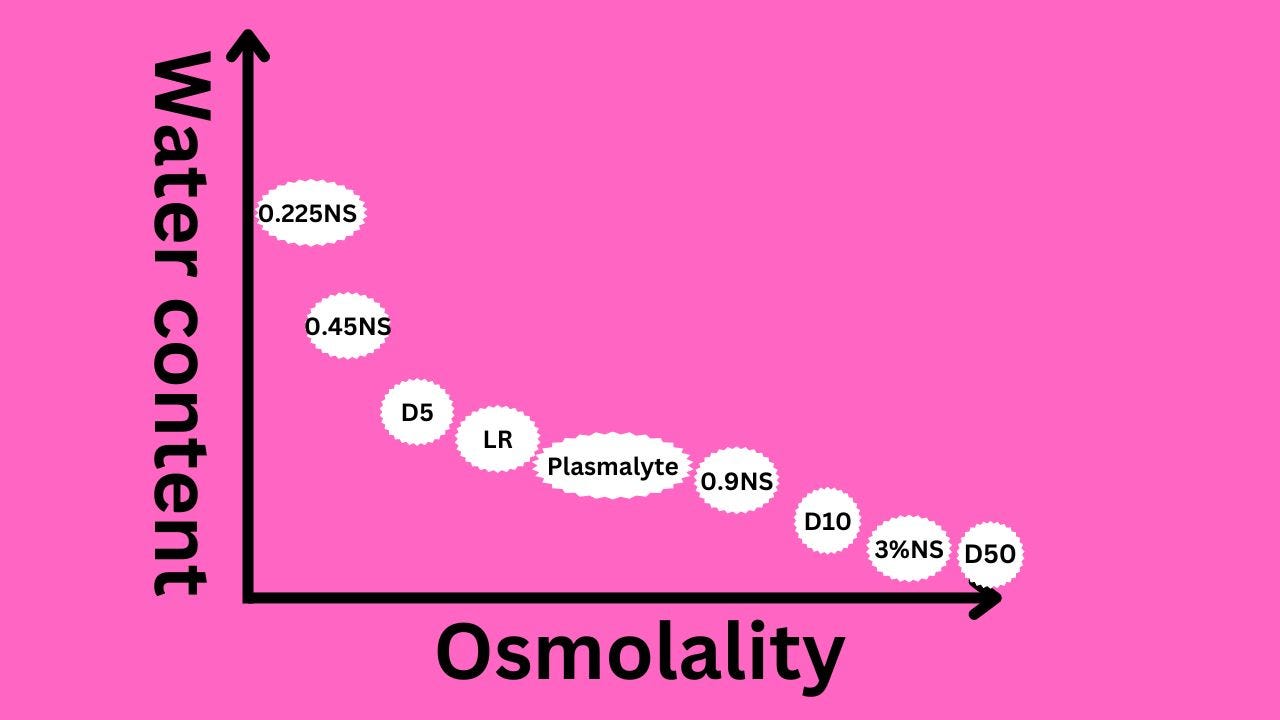
Osmolality
- 5% dextrose 252 mEq/L.
- 10% dextrose 504 mEq/L.
- 50 % dextrose 2520 mEq/L.
Once infused
Dextrose solutions stimulate insulin leading to glucose cell absorption and only free water left in the ECF. Insulin shifts potassium intracellularly which leads to hypokalemia.
Sodium bicarb solutions
Ingredients:
- 8.4 gm of NaHCO3.
- 100 ml of free water.
Osmolality:
200 mEq/100 ml ( 100 Na + 100 HCO3)
Mixing HCO3 drip:
- Bicarb ampule or push is a 50 ml prefilled syringe = 100 mEq (50 Na + 50 HCO3)
- Mix 3 amps in 1000 ml of free water = 300 mEq/L (Isotonic).
- Mix 3 amps in 1000 ml of 5% dextrose = 300 + 252 mEq/L = 552 (hypertonic but becomes isotonic once infused as glucose gets avidly absorbed by the cell).
- Mix 1.5 amps in 1000 ml of 0.45 NS = 150 + 154 = 304 mEq/L (Isotonic).
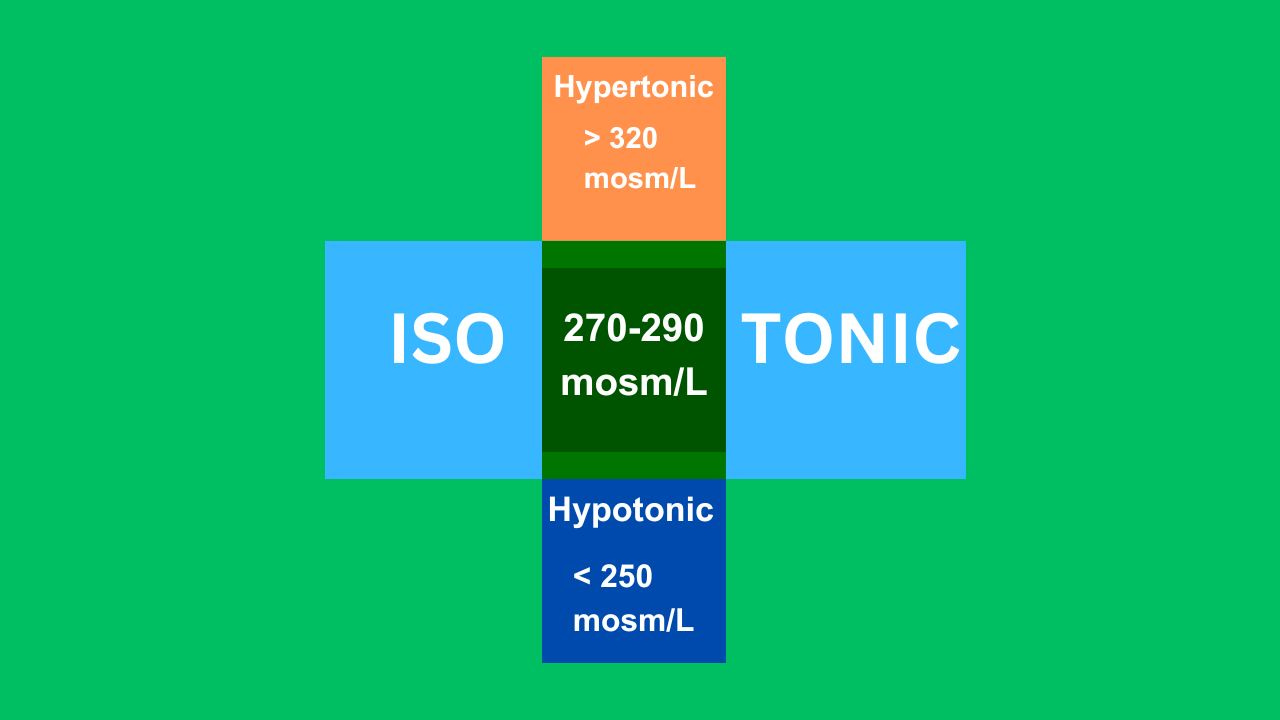
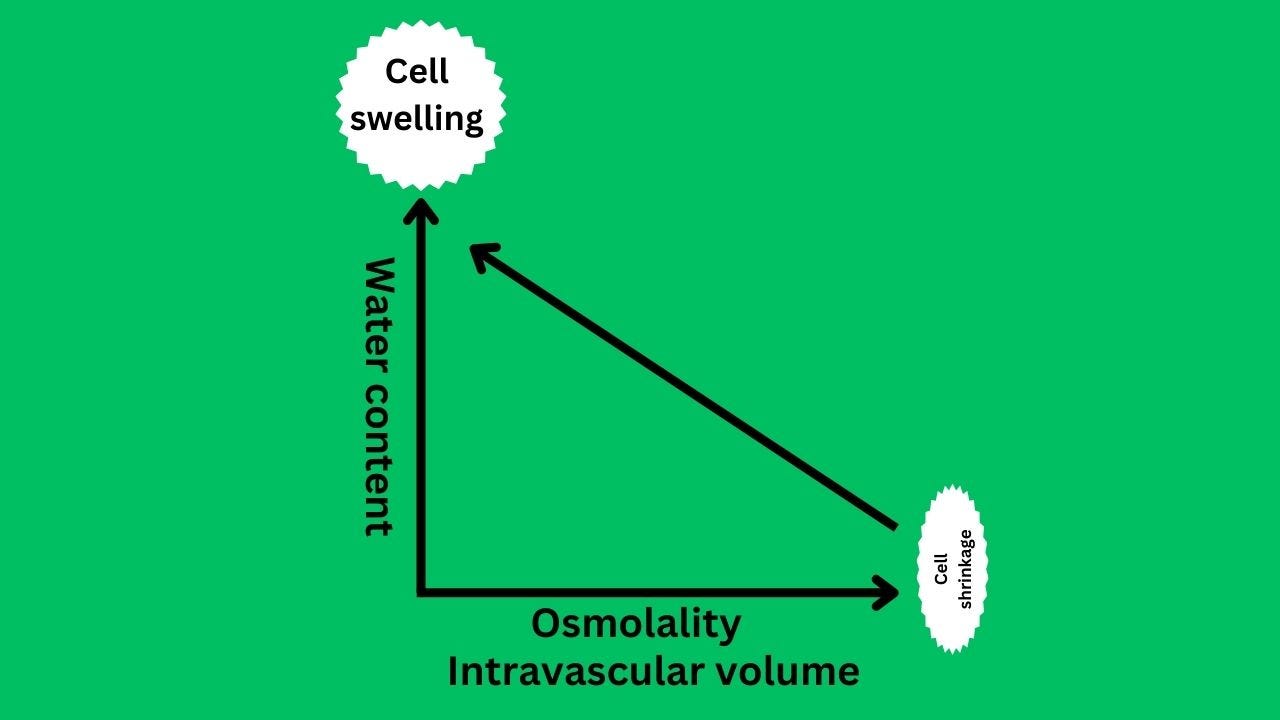
Osmolality and tonicity
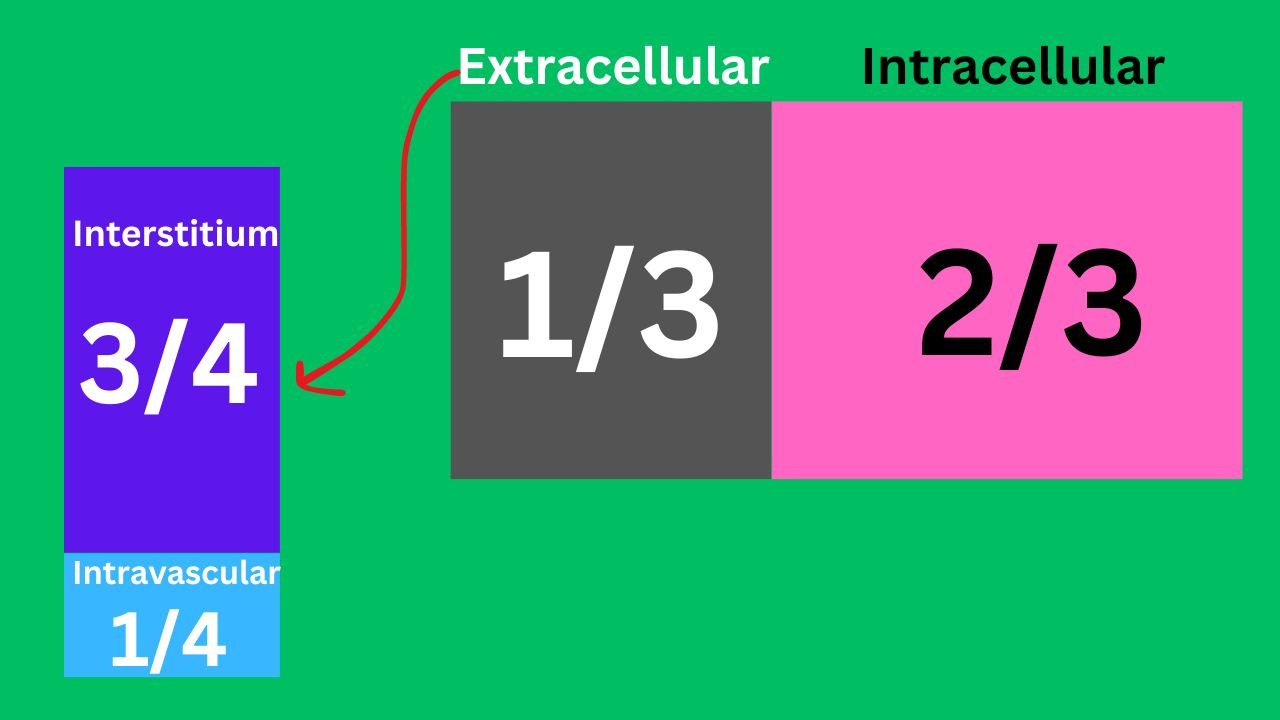
Fluid distribution in our body






Eight EKG patterns in acute MI we can’t afford to miss!
The top three antiemetics I rely on!
The use of 3% NS in hyponatremia, when and how.
The inpatient treatment of hypercalcemia
Hyperkalemia-induced EKG changes
The Proper Way to Replace Magnesium
Non-insulin diabetic medications
Chest Tubes & Pigtails: 5 Must-Know Tips for ICU Rotation